Description
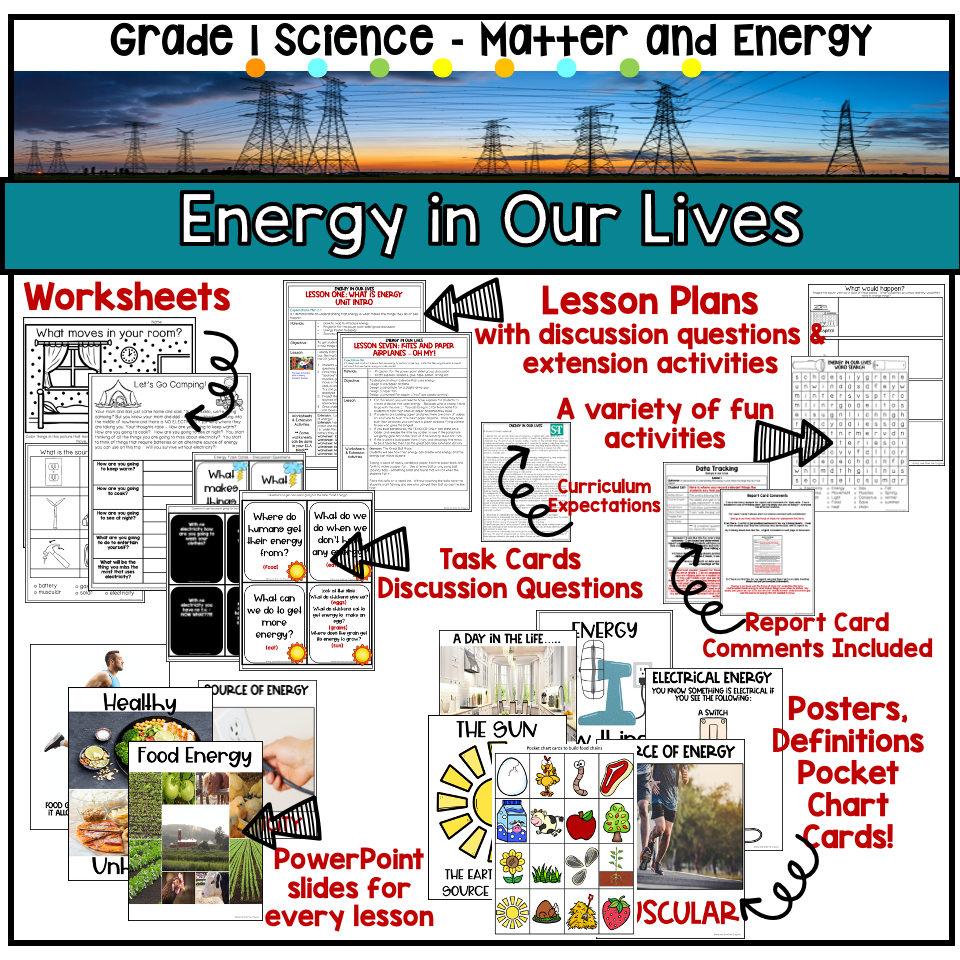
Do you want a fun and hands-on unit to teach Energy in our lives? This unit fits into the Matter and Energy curriculum in Ontario and is full of fun and engaging activities for little learners!
- This resource contains a PowerPoint slide(s) and a lesson plan for each lesson. There are extension activities as well as discussion questions (task cards) provided in these lesson plans.
- There is a section on report card comments where sample comments are provided and data tracking sheets included.
- There are posters, definitions and pocket chart cards with graphics for display and use in your science center or science bulletin board.
Included in this resource are the following worksheets and activities:
- What is energy
- how things move, what moves things, sources of energy, types of energy
- 6 worksheets
- task cards, posters, 9 Powerpoint slides
- The sun as energy
- Solar energy, The sun as a source of energy, The sun as the primary source of energy, What the sun does for living things and the importance of the sun
- 4 worksheets
- Extension activities, PowerPoint slide, poster, task cards, discussion questions
- Food as energy
- Sun’s importance to our food and survival, Food as a source of energy for living things
- 3 worksheets
- 2 PowerPoint slides, task cards/discussion questions, pocket chart activity for food chains, poster
- Electrical energy – Everyday use of energy
- Our daily use of energy, conservation of electricity, consumption of electricity, being aware of our use of energy and ways to save/conserve energy, becoming efficient and not wasteful, WHY it is important to reduce our use of energy
- 6 worksheets
- 2 PowerPoint slides, 3 posters/vocabulary/definitions
- Safety in regards to energy
- 1 worksheet, 7 PowerPoint slides
- What would you do if there were no electricity (power outage)
- A day without electricity, alternate energy sources, alternate activities if there is no electricity, going back to the “old” days
- 5 worksheets
- 1 Powerpoint slide, task cards/discussion questions
- Design and construct an energy device
- hands-on activity/project
- Seasonal uses of energy
- different uses of energy during different seasons/temperatures, ways to use alternative energy to conserve energy during the different seasons
- 1 PowerPoint slide, task cards/discussion questions, 1 worksheet
BONUS
- Energy word search
IMPORTANT TO NOTE:
**For this unit I have included worksheets that can be used in your ELA program. There are reading comprehension worksheets for most lessons as well as a wide variety of writing activities you can also incorporate for a cross-curricular delivery of this unit.
This unit covers the following Ontario Curriculum expectations:
1.1 describe their own and their family’s uses of energy (e.g., to operate lights, video games, cars, computers); identify ways in which these uses are efficient or wasteful, taking different points of view into consideration (e.g., the point of view of a parent, a sibling, a member of their extended family); suggest ways to reduce personal energy consumption, and explain why it is important for people to make these choices
1.2 describe how the everyday lives of different people and other living things would be affected if electrical energy were no longer available (e.g., families, farmers, businesses and stores, a company that offers alternative energy sources such as solar-powered devices, the plants in a hydroponic greenhouse, the tropical animals in a Canadian zoo)
2.1 follow established safety procedures during science and technology investigations (e.g., keep workspaces neat and tidy by putting all tools, materials, and equipment back where they belong)
2.2 investigate how the sun affects the air, land, and/or water, using a variety of methods (e.g., standing outside on a sunny and a cloudy day and noting the differences; putting a dish of water in the sun and the shade and observing what happens) and resources (e.g., books, videos/ DVDs, CD-ROMs, the Internet)
2.3 design and construct a device that uses energy to perform a task (e.g., a kite that flies using the wind; a musical instrument that uses human energy to make sounds)
2.4 investigate and compare seasonal differences in the ways we use energy and the types of energy we use (e.g., we keep warm in winter by wearing a sweater and using furnaces and woodstoves; we stay cool in summer by sitting in the shade or going to places that are air-conditioned; we adjust the amount of light we need by opening or closing the curtains and turning lights on or off)
2.5 use scientific inquiry/experimentation skills (see page 12), and knowledge acquired from previous investigations, to explore the effects of light and heat from the sun (e.g., by growing plants in the presence and absence of sunlight; by feeling the temperature of dark papers that have been in the sun and in the shade; by covering a portion of a piece of colored paper and exposing the paper to the sun)
2.6 investigate how the sun’s energy allows humans to meet their basic needs, including the need for food (e.g., trace the flow of energy from the sun, which provides energy to plants, which make food for animals to eat, and then from plants and animals, which provide food for humans to eat)
2.7 use appropriate science and technology vocabulary, including explore, investigate, design, energy, and survival, in oral and written communication
2.8 use a variety of forms (e.g., oral, written, graphic, multimedia) to communicate with different audiences and for a variety of purposes (e.g., use labeled diagrams to show what happened when plants were grown in varying light conditions)
3.1 demonstrate an understanding that energy is what makes the things they do or see happen
3.2 demonstrate an understanding that the sun, as the earth’s principal source of energy, warms the air, land, and water; is a source of light for the earth; and makes it possible to grow food
3.3 identify food as a source of energy for themselves and other living things
3.4 identify everyday uses of various sources of energy (e.g., food to help animals, including humans, survive and move; natural gas to heat homes and schools; petroleum to power cars and buses; electricity to power lights; batteries to power toys)
3.5 demonstrate an understanding that humans get the energy resources they need from the world around them (e.g., the wood, oil, and gas to heat our homes and cook our food) and that the supply of many of these resources is limited so care needs to be taken in how we use them
Copyright © Laura Merritt – Stop and Smell the Crayons (Tpt) All rights reserved by the author. This product is to be used by the original downloader only. Copying for more than one teacher, classroom, department, school, or school system is prohibited. This product may not be distributed or displayed digitally for public view. Failure to comply is a copyright infringement and a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). Clipart and elements found in this PDF are copyrighted and cannot be extracted and used outside of this file without permission or license. Intended for classroom and personal use ONLY. See product file for clip-art and font credits.
CHECK OUT MY OTHER GRADE ONE SCIENCE UNITS
Energy in Our Lives
Needs and Characteristics of Living Things
Materials, Objects and Everyday Structures
Earth and Space Systems – Daily and Seasonal Changes
Terms
Copyright © Laura Merritt – Stop and Smell the Crayons (Tpt) All rights reserved by the author. This product is to be used by the original downloader only. Copying for more than one teacher, classroom, department, school, or school system is prohibited. This product may not be distributed or displayed digitally for public view. Failure to comply is a copyright infringement and a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). Clipart and elements found in this PDF are copyrighted and cannot be extracted and used outside of this file without permission or license. Intended for classroom and personal use ONLY. See product file for clip-art and font credits.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.